本文项目已发布到github,后续学习项目也会添加到此工程下,欢迎fork点赞。https://github.com/wangyuheng/spring-boot-sample
国际化
简单来说,国际化就是让应用(app、web)适应不同的语言和地区的需要,比如根据地区选择页面展示语言。
i18n =internationalization,首末字符i和n,18为中间的字符数
原理 基于传入语言or地区 标识进行判断,输出不同内容。伪代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 func hello (var lang) { if (lang == "にほんご" ) { return "おはよう" ; } else if (lang == "English" ) { return "hello" ; } else { return “你好” } }
原理简单,但是如何优雅的实现?spring是否已经提供了现成的轮子?答案是肯定的。基于原理可以认为,实现国际化主要分为2部分
输入语言or地区 标识
输出不同语言or地区的内容文案
输出 通过MessageSource实现不同语言输出。
在spring初始化refresh过程中,会初始化MessageSource。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext , DisposableBean {... @Override public void refresh () throws BeansException, IllegalStateException synchronized (this .startupShutdownMonitor) { prepareRefresh(); ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); initMessageSource(); initApplicationEventMulticaster(); onRefresh(); registerListeners(); finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); finishRefresh(); } ... }
而springboot会初始化ResourceBundleMessageSource实例作为MessageSource的默认实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Configuration @ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = MessageSource.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) @AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE) @Conditional(ResourceBundleCondition.class) @EnableConfigurationProperties @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages") public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration ... @Bean public MessageSource messageSource () ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); if (StringUtils.hasText(this .basename)) { messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray( StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this .basename))); } if (this .encoding != null ) { messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this .encoding.name()); } messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this .fallbackToSystemLocale); messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this .cacheSeconds); messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this .alwaysUseMessageFormat); return messageSource; } ... }
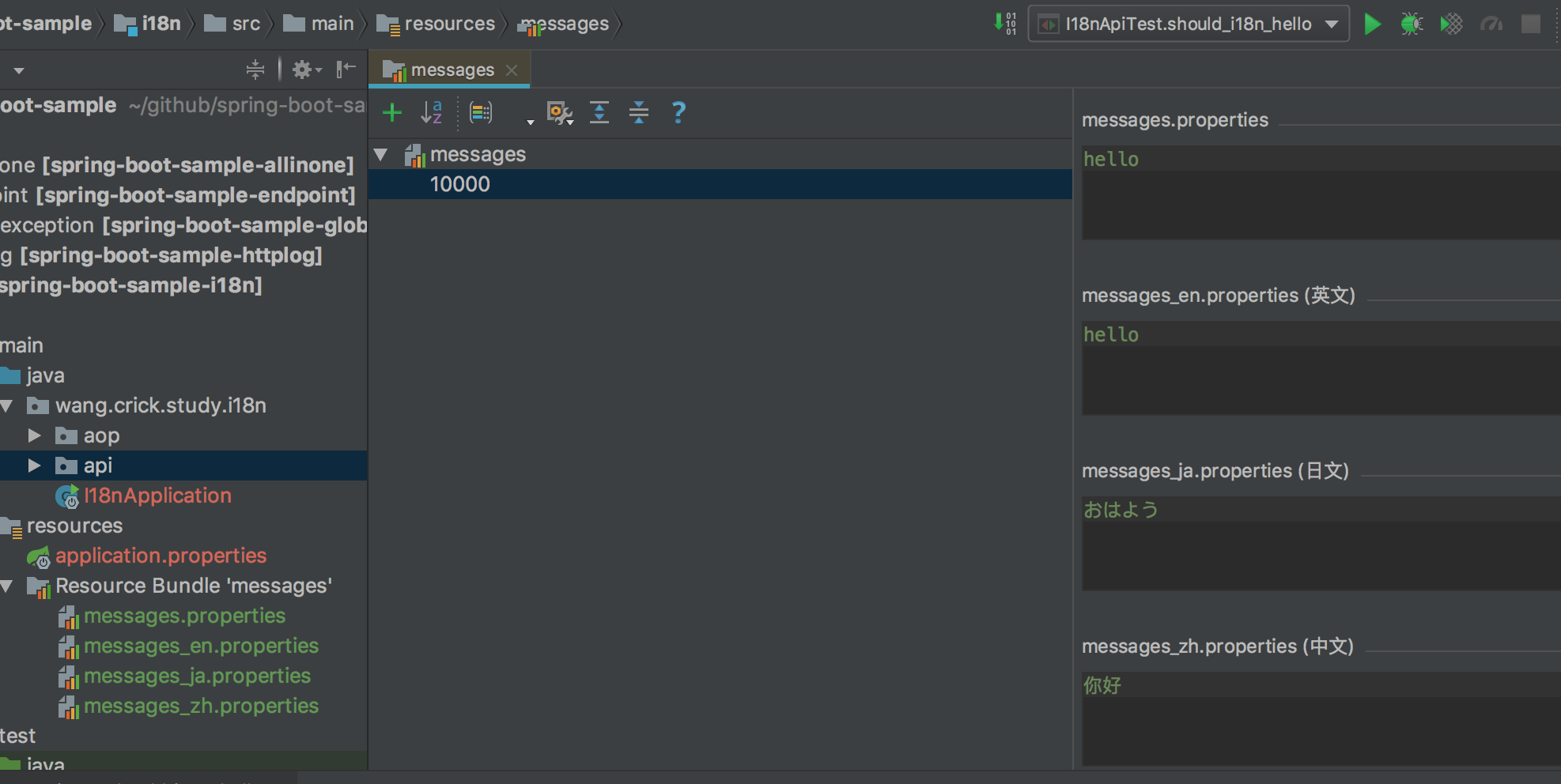
MessageSource内部则通过basename以及Locale定位到具体Resource Bundle文件,并基于code**(properties key)**读取对应的显示文本。
其中涉及到的三个概念
basename标识
Locale
Resource Bundle
basename 用于指定Resource Bundle文件位置,可以通过配置文件配置, 默认为messages
1 spring.messages.basename =messages
Locale Locale对象代表具体的地理,政治或文化地区,用来指定语言及地区。构造函数如下
1 2 3 4 5 Locale(String language) Locale(String language, String country) Locale(String language, String country, String variant)
variant 变体值,用于指示变化的任意值Locale。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 static public final Locale ENGLISH = createConstant("en" , "" );static public final Locale CHINESE = createConstant("zh" , "" );static public final Locale SIMPLIFIED_CHINESE = createConstant("zh" , "CN" );static public final Locale TRADITIONAL_CHINESE = createConstant("zh" , "TW" );
Resource Bundle ResourceBundle类和Properties类似,都可以读取程序内的文件,不过ResourceBundle更强大,提供了诸如缓存、Locale区分一类的操作。
所以MessageSource 其实是对ResourceBundle的一种封装增加,优化了使用,并且托管与spring容器生命周期。这时就有一个很重要的选择:
如果通过静态类封装了restful的接口返回,可以自己扩展ResourceBundle类,而不是将MessageSource的spring实例放置在静态类中。
而idea中提供了Resource Bundle资源束的支持,方便用户添加管理国际化文案。
输入 看完输出的形式,可以知道,我们只需要确认Locale就可以实现国际化。所以我们再找一下Locale的轮子。
accept-language servlet自带轮子,基于http协议,即通过header中的accept-language 报文头,实现Locale的自动识别。
代码见org.apache.catalina.connector.Request
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public class Request implements org .apache .catalina .servlet4preview .http .HttpServletRequest @Override public Locale getLocale () if (!localesParsed) { parseLocales(); } if (locales.size() > 0 ) { return locales.get(0 ); } return defaultLocale; } protected void parseLocales () localesParsed = true ; TreeMap<Double, ArrayList<Locale>> locales = new TreeMap<>(); Enumeration<String> values = getHeaders("accept-language" ); while (values.hasMoreElements()) { String value = values.nextElement(); parseLocalesHeader(value, locales); } for (ArrayList<Locale> list : locales.values()) { for (Locale locale : list) { addLocale(locale); } } } }
spring提供的轮子
LocaleResolver 实现次接口,用于自定义解析规则
RequestContextUtils 基于request获取Locale,优先使用自定义LocaleResolver
LocaleContextHolder通过ThreadLocal持有Locale对象,在FrameworkServlet支持servlet.service时执行初始化。
LocaleChangeInterceptor通过Configuration配置Locale切换规则
综上,只要请求方在header中增加了accept-language 报文头,即可在代码中通过LocaleContextHolder获取Locale对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;@SpringBootApplication @RestController public class I18nApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(I18nApplication.class, args); } @Autowired private MessageSource messageSource; @GetMapping("hello") public Object hello (HttpServletRequest request) return messageSource.getMessage("10000" , new Object[]{}, LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()); } }
lang 除了accept-language外,常见在url中增加了国家及地区参数,如: https://twitter.com/?lang=zh
通过lang 配置国际化,需要通过LocaleChangeInterceptor 进行配置,此配置的优先级高于accept-language
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @Configuration public class I18nConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter @Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver () SessionLocaleResolver sessionLocaleResolver = new SessionLocaleResolver(); return sessionLocaleResolver; } @Bean public LocaleChangeInterceptor localeChangeInterceptor () LocaleChangeInterceptor localeChangeInterceptor = new LocaleChangeInterceptor(); localeChangeInterceptor.setParamName("lang" ); return localeChangeInterceptor; } @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) registry.addInterceptor(localeChangeInterceptor()); } }
Test Case 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 import org.junit.Test;import org.junit.runner.RunWith;import org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.LocalServerPort;import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;import org.springframework.context.i18n.LocaleContextHolder;import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;import java.util.Locale;import java.util.ResourceBundle;import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(webEnvironment=SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class I18nApiTest @LocalServerPort private int port; private TestRestTemplate restTemplate = new TestRestTemplate(); @Test public void should_return_message_by_different_accept_language () throws Exception HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.add("accept-language" , "en" ); HttpEntity entity = new HttpEntity(headers); ResponseEntity<String> resultEn = restTemplate.exchange("http://localhost:" +port+"/hello" , HttpMethod.GET, entity, String.class); assertEquals("hello" , resultEn.getBody()); headers.remove("accept-language" ); headers.add("accept-language" , "zh" ); entity = new HttpEntity(headers); ResponseEntity<String> resultCh = restTemplate.exchange("http://localhost:" +port+"/hello" , HttpMethod.GET, entity, String.class); assertEquals("你好" , resultCh.getBody()); } @Test public void should_return_zh_message_by_accept_language_zh_locale () LocaleContextHolder.setLocale(Locale.CHINA); assertEquals("你好" , ResourceBundle.getBundle("messages" , LocaleContextHolder.getLocale()).getString("10000" )); } @Test public void should_return_zh_message_by_different_lang () String lang = "en" ; ResponseEntity<String> resultEn = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:" +port+"/hello?lang=" +lang, String.class); assertEquals("hello" , resultEn.getBody()); lang = "zh" ; ResponseEntity<String> resultCh = restTemplate.getForEntity("http://localhost:" +port+"/hello?lang=" +lang, String.class); assertEquals("你好" , resultCh.getBody()); } @Test public void should_return_by_lang_when_set_lang_and_accept_language () String lang = "zh" ; HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.add("accept-language" , "en" ); HttpEntity entity = new HttpEntity(headers); ResponseEntity<String> resultEn = restTemplate.exchange("http://localhost:" +port+"/hello?lang=" +lang, HttpMethod.GET, entity, String.class); assertEquals("你好" , resultEn.getBody()); } }
LanguageTagCompliant Locale的命名规则为 lang-country, 如: zh-CN ,有时会看到zh_CH 这种写法,这是另一种规范,可以在CookieLocaleResolver了解规范定义
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @UsesJava7 protected Locale parseLocaleValue (String locale) return (isLanguageTagCompliant() ? Locale.forLanguageTag(locale) : StringUtils.parseLocaleString(locale)); }
需要在中LocaleChangeInterceptor开启兼容模式
1 localeChangeInterceptor.setLanguageTagCompliant(true );
但是为了符合规范,不推荐zh_CH 这种写法。
倾向 按照《Http参数格式约定》 文中所述,通用&非业务参数,一般会选择放到header中,所以比较倾向于accept-language 这种定义方法。